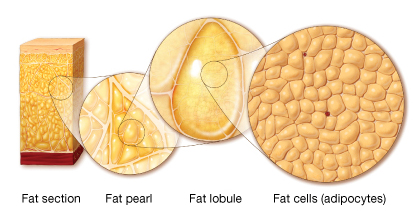
Adipose tissue is the most secure and easily accessible source of autologous (own) cells with multipotent properties (able to repair any tissue) and with high potential.
In general the researchers are warryregarding some aspects of cell therapy, however, methods of study and the technology of fat stem cells (HBC) are constantly improved. The results of long-term clinical trials in different countries confirm the prospects of HBC for many areas of regenerative medicine.
In today’s cellular regenerative medicine technologies extend to the lead position. Prospects of cell therapy for the treatment of many diseases attracted the attention of researchers and practitioners all over the world. Stem cells play the role of a tool able to restore damaged tissue and correct the dysfunction of organs.
No risk
As a source of stem cells various tissues in the bodycan serve, from bone marrow – to the tooth pulp and the hair follicle, and technology of therapeutic cloning, induction of pluripotency or transdifferention of cells suggest the possibility of obtaining stem cells from the already specialized ones. Procedures for obtaining and application of stem cells are rather expensive, but still the major limitation of introduction of modern methods of cell therapy is their safety, including, first of all, the medical aspect, as well as ethical and legal components.
For this reason, among a wide variety of types of stem cells that are available to the clinic, in recent years the most interesting became stem cells from adipose tissue.
- First, this therapy uses only person’s own tissues and cells, so there is no risk of infection with transmisable diseases.
- Second, it is fully compatible with person’s own cells regarding chromosome and gene structure, and hence there will not be allergic or immune conflict.
- Third, there is no risk of complications of cancer, because HBC are mature enough for this, as opposed to embryonic SC, which often cause them.
- Fourth, only a small amount of adipose tissue is needed to release the necessary amount of IC. Therefore, after activation the SC can be entered directly back to the patient without the need for being grown on substances (embryonic SC are grown for several months).
What is a stem cell? From which tissues we can receive them?
Stem cells are non-specialized or undifferentiated cells, capable of two processes: self-renewal and differentiation/specialization.
Adult stem cells:
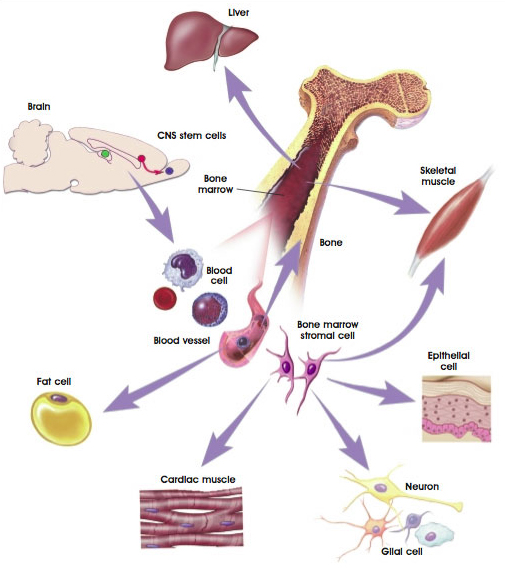
- Bone Marrow
- Nuclear transfer
- Adipose tissue
- Peripheral blood
- Muscle
- Brain
- Blood vessel
- Liver
- Skin
Differentiation
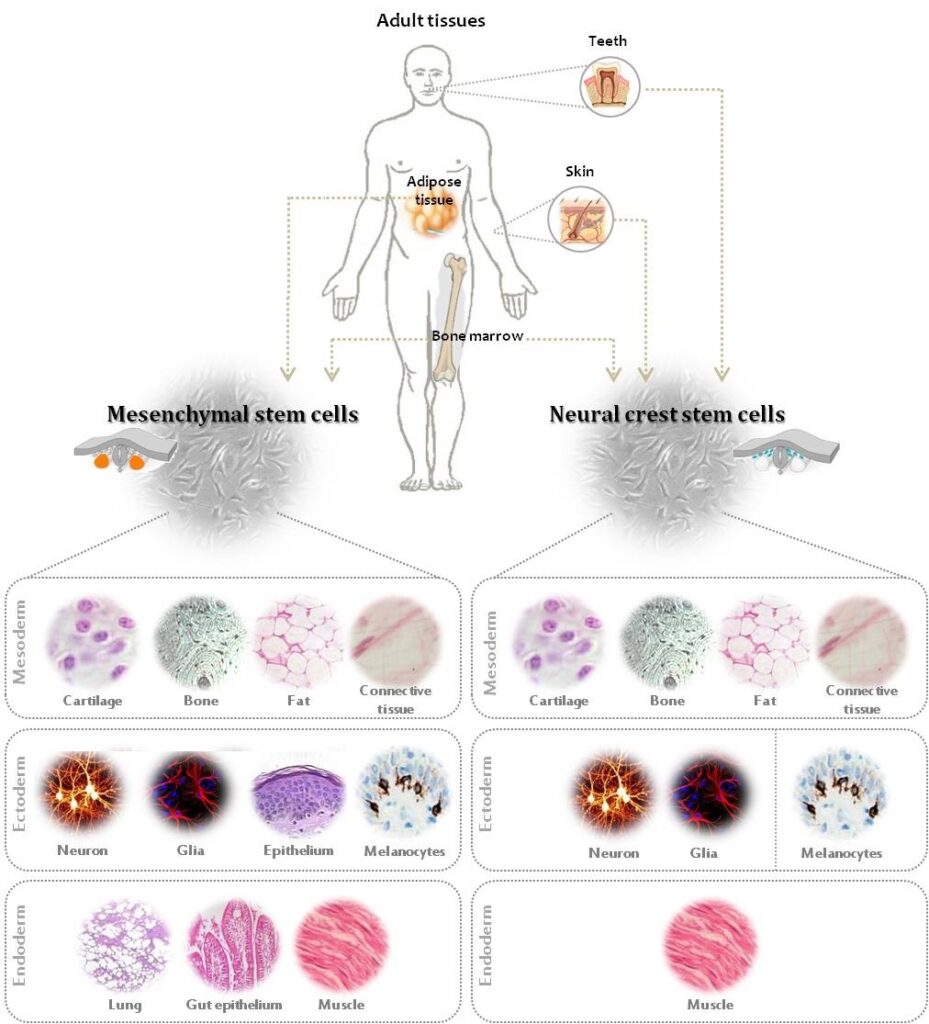
Why fat?