An alternative method to flap and implant-based breast reconstruction, known as autologous fat grafting, has been successfully implemented for more than 15 years. Lipografting is a method where a patient’s own tissue is transplanted in order to correct breast shape after mastectomy related to breast cancer.
The essence of the method is that adipose tissue is taken by liposuction from places where there is an excess of subcutaneous fat, and through small punctures it is introduced into the area of the removed breast. The result of the procedure is the rebuilding of breast volume, as well as the restoration of symmetry with the opposite breast.
In the process of reconstruction, no new scars are formed, and the minimal trauma of the operation allows patients to return to normal life the next day after the procedure. With proven oncological safety and effectiveness, along with the simplicity of the technique of fat transplantation and low risk of complications, autologous fat grafting has become an enticing option for patients following mastectomy.
Get a free online consultation
Contact our doctor to learn whether lipografting could work for you >>>

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Fat Grafting for Breast Reconstruction
Transfer of autologous adipose tissue to the breast area is used:
• to correct the consequences of post-surgical deformations (due to operations for breast cancer);
• for women undergoing preventive breast amputation;
• for correction of congenital deformation (e.g., Poland syndrome);
• in cases of absence of breast as a result of burns, injuries, etc.;
• in cases of breast tissue underdevelopment caused by medical manipulations (removal of hemangiomas, skin tumors, etc.).
The purpose of such treatment as fat grafting is both to restore the volume and shape of the breast, and to create symmetry with the opposite breast. Lipotransfer can also be used along with breast implants to correct shape and create a more natural appearance.
Results
Fat grafting allows complete restoration in volume and shape of the removed breast, as well as the restoration of symmetry. The result is visible immediately after surgery, although the final volume and shape should be evaluated no earlier than 3 months after lipofilling. The results are stable and are preserved regardless of changes in body weight.
Immediate satisfaction, low trauma and the absence of breast implants have become powerful motivators for patients to request this regenerative surgery. From an aesthetic point of view, patients receive a more natural contour and softness of the breast compared to conventional silicone implants.
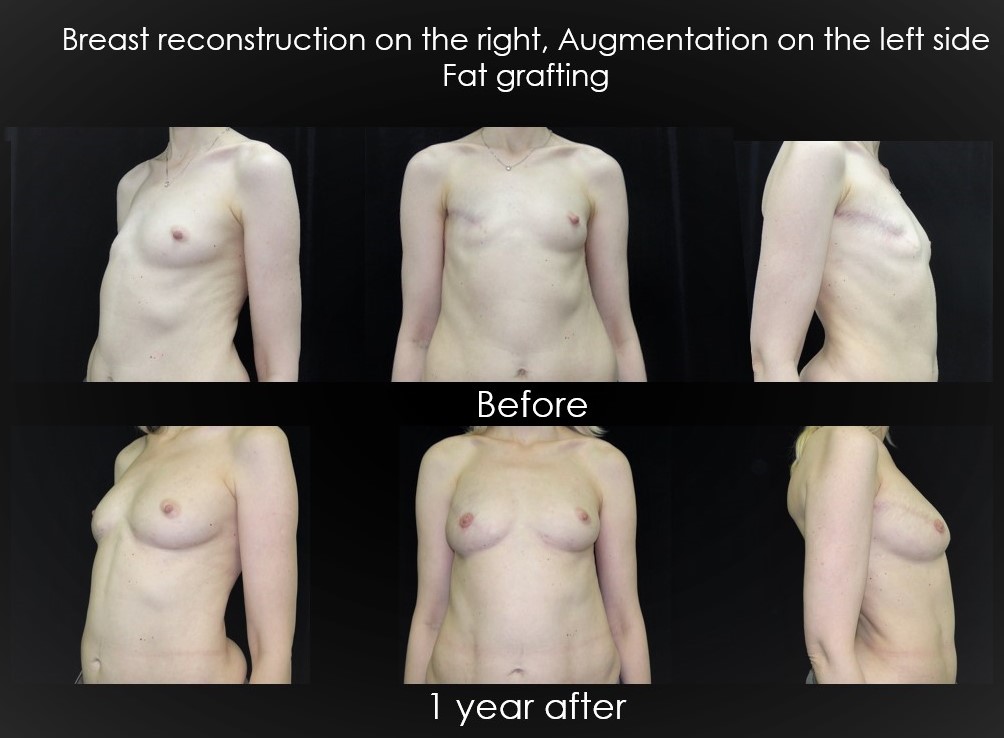
It should be noted that a single operation in most mastectomy cases is not enough to grow the required amount of tissue, since part of the adipose tissue after the transplantation procedure tends to be lost to partial resorption. Therefore, several steps may be required to achieve the desired result. While multiple steps may seem unappealing, there are advantages to this method. Since the step-by-step addition of volume allows literal sculpting of a new breast, the result of reconstruction by lipografting in the vast majority of cases significantly exceeds the quality of the results obtained by other methods.
According to independent studies, the vast majority of patients were satisfied with the results of fat transplantation. These patients confirmed that they would be willing to undergo the fat transplant procedure again and would recommend the procedure to others.
Contact us
Get a free doctor consultation to learn whether breast grafting could be beneficial to you >>>

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
How the Procedure of Fat Grafting Is Performed
Lipografting is a very common medical procedure. In 2014, it was reported that more than 25,000 fat transfer procedures were performed (according to the data of Members of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, ASPS).
During the procedure, adipose tissue is taken from the patient from areas where it is present in large quantities (abdomen, hips, etc).
Based on the desired volume of correction, the required amount of lipoaspirate is taken into syringes with the liposuction cannula. Then, if necessary, the harvested material is processed in a centrifuge or by other methods. After that, the purified fat is placed in syringes and aseptically injected into the correction area, using special micro-cannula for implantation.
For successful engraftment of the injected material, fat is implanted into several tunnels through several different channels. This preserves the integrity of the grafted fat and maximizes the contact surface between the lipoaspirate and the capillaries of the patient. Diffusion of nutrients from nearby capillaries is necessary for the survival of adipocytes (adipose tissue cells) and promotes their integration with the surrounding tissue.
Both the harvesting and the subsequent introduction of adipose tissue is completed in a day, which does not require a long stay in the clinic. In addition, the recovery period after such a procedure is usually typically just one day. The day after the procedure, patients can return to the usual household tasks and can return to active sports in 2 weeks. Wearing compression underwear after this procedure is also generally not required.
The full recovery process is completed in an average of 6 months. As a result of the procedure, about 60-70% of the fat engraftment volume is maintained, and this volume is preserved for life.
Side Effects of Fat Transfer Breast Reconstruction
Complications related to fat grafting for breast reconstruction are quite rare and usually easily managed. General surgical complications (infection, hematoma, seroma, etc.) occur in less than 1% of patients, which is significantly lower when compared to implant-based or flap surgery.
Overall, patients are satisfied with the fat transfer procedure. In rare cases, however, complications are possible 5-6 months after the intervention, including infection, fat necrosis, calcification and cyst formation in the reconstructed breast. In the vast majority of cases, these postoperative formations have clear differences from malignant tumors (according to ultrasound, mammography, MRI) and do not require additional diagnostic examinations. Rarely, in contentious cases, puncture or open biopsy is necessary.
In the long-term period, adverse events such as infections and skin necrosis were not observed and continuous improvements of lipografting techniques reduce the prevalence of side effects.
Contraindications for Fat Transfer
Contraindications to the use of lipografting for breast reconstruction include:
- the presence of cancer or suspicion of it;
- acute infectious disease;
- contraindications to anaesthesia and/or high risk of bleeding;
- pathological processes in the area of the proposed surgery.
A relative contraindication is the lack of fat deposits in donor areas. Such cases are rare and can occur with a body mass index (BMI) below 18.

The Safety of Breast Reconstruction with Fat Grafting
Available clinical data confirms the oncological safety of lipografting for breast reconstruction in patients undergoing treatment for breast cancer.
The risk of developing a local or systemic recurrence of cancer in patients who underwent lipografting is not greater than in patients in whom breast reconstruction was not carried out at all.
Summary:
Fat grafting is a method that has proven to be safe and has good results in patients with amastia due to breast cancer. Lipofilling restores the volume and shape of the breast with long-term aesthetic results. The procedure uses gentle techniques, utilizing autologous tissue and requiring minimal recovery time.
Contact us
Get a free doctor consultation to learn whether breast grafting could be beneficial to you >>>

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor