High blood pressure (HBP), which according to scientific terminology is named hypertension, is perhaps one of the most insidious diseases. Though hypertension usually starts and progresses without symptoms, it is regarded as the leading cause of heart failure, cerebrovascular stroke, severe renal impairment, vision loss, cognitive function impairment and other issues. According to the World Health Organization, it is one of the major causes of premature death worldwide.
You can be diagnosed with hypertension if your blood pressure figures, i.e., the strength with which blood pushes against the walls of arteries, are 140/90 or higher measured three times on different days.

The disease is classified into two types:
- essential or primary type;
- secondary type.
The first type of the disease is not connected to any distinct underlying medical causes. It includes about 90% of all cases globally. The remaining 10% of cases are ascribed to the secondary type of the pathology. In this instance, hypertension is caused by other health problems.

Elevated blood pressure for too long of a period damages the walls of arteries and further leads to atherosclerosis (the formation of plaques due to the accumulation of fat and calcium), which causes the narrowing of arteries and increases blood pressure even more. Among other consequences of hypertension, the heart becomes overloaded and worn-out. The accumulation of plaques leads to artery blockage and further deterioration of blood flow through the heart muscle. A lack of oxygen and nutrients caused by poor blood supply may damage part of the heart muscle and result in myocardial infarction.
In this article, we discuss common treatment methods for hypertension, as well as modern approaches utilizing stem cells.
Treatment of Hypertension
In the early days, after being diagnosed with hypertension, you may get recommendations from your doctor to change your lifestyle and habits in order to control your blood pressure. The following measures may be effective for a rather long period:
- a healthy diet with less salt;
- regular and feasible physical activity;
- healthy weight control or losing weight;
- giving up alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking.
However, for many patients, these efforts are too difficult to implement due to established habits or the inability to make changes in their usual way of life. Thus, the disease progresses, and treatment using medication is required.
The following medications and their combinations are usually prescribed for patients with hypertension:
- thiazide diuretics
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
- calcium channel blockers
- alpha blockers
- alpha-beta blockers
- beta blockers
- aldosterone antagonists
- renin inhibitors
- vasodilators
- central-acting agents
In general, antihypertensive drugs lower blood pressure either through relaxing the walls of blood vessels or increasing the elimination of salt and water by the kidneys. At the same time, drugs from the group of beta blockers reduce heart rate and force the heart to beat with less force.
Even if patients take their medications exactly as prescribed and the combination includes three of four types of high blood pressure medications, the control may be not achieved, and the high blood pressure may persist. Besides, most of these drugs have haunting side effects, such as headaches, dizziness, rashes, constipation, increased thirst, needing to go to the toilet frequently, and others, which may negatively affect the quality of life.
Stem Cells in Cardiovascular Therapy
Patients with hypertension have to undergo antihypertensive therapy for the rest of their lives, facing the tolerance issues of these medications and side effects they cause. However, there is a recent approach which improves the state of blood vessels, stimulates the regeneration of damaged tissues and exerts the overall rejuvenating effect on the body. We are talking about stem cell-based treatment, also known as regenerative medicine.
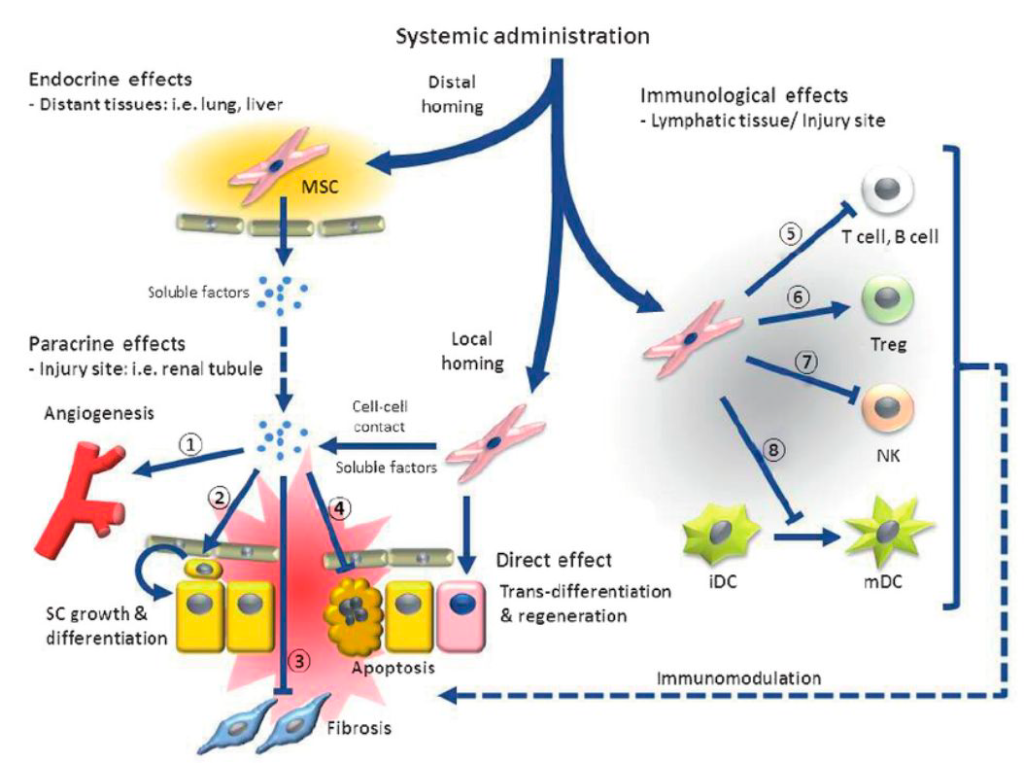
Regenerative approaches to cardiovascular therapy have been studied for several decades. The most convenient, safe and widely studied method includes the administration of adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are rather easy to obtain and cultivate. According to the latest data, this type of stem cell produces such active substances as growth factors, cytokines, exosomes, and microRNAs, which boost the regenerative processes in injured heart muscle and vessels.
MSCs also stimulate the process of new vessel formation and the restoration of damaged vessels, contributing to the improvement of blood flow and nutrient supply in the heart muscle as well. According to other studies, transplanted stem cells stimulate the recruitment of an internal pool of endogenous stem cells. Thus, these lead to rejuvenation of all the body’s tissues, including cardiovascular tissue.
Overall Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment
Cell-based therapy supposes intravenous or local delivery of the patient’s own or donor stem cells. The introduced cells reach damaged areas and stimulate regeneration processes locally, producing biologically active molecules. This also improves the general physical state. The therapeutic effect of MSCs was proved in neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, endocrinological, musculoskeletal and other disorders.
Contact us
Learn whether stem cells would help in your personal case.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Modulation of Inflammation
Another possible way that MSCs act in controlling blood pressure is by reducing the inflammation level. It is known that hypertension provokes the increase of proinflammatory cytokines, thus increasing the risk of blood vessel clotting. The anti-inflammatory potential of MSCs was demonstrated in both in vitro and in vivo studies.
Role in Atherosclerosis
The anti-inflammatory mediators produced by MSCs contribute to their positive effect toward atherosclerotic lesions, as well as the improvement of the function of the damaged internal surface of blood vessel walls. It was shown that atherosclerosis is one of the most critical consequences of hypertension, and it is associated with the infiltration of inflammatory cells and an increased level of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The ability of MSCs to mitigate inflammation has been proven in a panel of clinical studies. Also proven was their role in modulating lipid levels, which is the key process in plaque formation and progression.
Hypoxic conditions, which are usual for tissues of hypertension patients, as their vessels are clotted with atherosclerotic plaques, are quite favorable for mesenchymal stem cells. They respond to low-oxygen microenvironments with increased proliferation (division rate) and develop features that are most beneficial for treatment purposes.
Assistance in Weight Loss
It is a well-known fact that increased weight is one of the major risk factors of hypertension. Often, weight loss is enough to control blood pressure. That’s why the ability of mesenchymal stem cells to decrease weight and correct obesity induced metabolic dysregulation is one of the most effective ways of treating hypertension.
Procedure and Safety Aspects
Stem cell hypertension treatment is based on the transplantation of healthy cells into damaged organs, blood vessels and surrounding tissues. Both the patient’s own stem cells and donated stem cells may be used for hypertension treatment.
Stem cells are harvested from adipose tissue or bone marrow and then cultivated and processed in a specific way to prepare unique cell products for transplantation. The process of obtaining cells from a patient’s body is safe and quick; small amounts of fat tissue or bone marrow are required for the therapy.
The procedure of cell product introduction through an IV drip takes less than an hour. Stem cell transplantation does not require general anesthesia. Our patients don’t suffer from any side effects, allergic reactions or immune reactions. The rare event of individual intolerance after administration, such as short-term fever, cannot be excluded, while the overall state of the patient is carefully monitored by our specialists during the procedure and several hours after.
Clinical studies have confirmed the high safety of mesenchymal stromal cells for use in cell-based therapy in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
At Swiss Medica, the best results are usually achieved by using a comprehensive approach, where stem cell therapy is combined with various methods, such as physiotherapy, oxygen therapy, reflexotherapy, ultraviolet or laser blood irradiation, and other methods, which promotes and supports the long-lasting regenerative effect of stem cells.
After Therapy
The effectiveness of stem cell treatment is assessed 1-3 months upon starting stem cell therapy as this time is needed for introduced cells to come in full force. However, most patients will experience improvements in the first weeks after the treatment. Based on the results, a follow-up plan will be proposed to the patient to meet their unique needs, and the clinic’s doctors always stay in touch to track their health status.
Would Stem Cell Therapy Fit Me?
Though stem cells are widely used in the treatment of certain diseases, their efficacy for all patients cannot be predicted and guaranteed without comprehensive preliminary medical examination. The effectiveness of the therapy depends on multiple factors, including the stage of the disease, patient’s age, the patient’s lifestyle, etc. You can find information about whether stem cell therapy is appropriate for your case, as well as about possible results and treatment issues.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of the treatment, its cost and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor